HAS
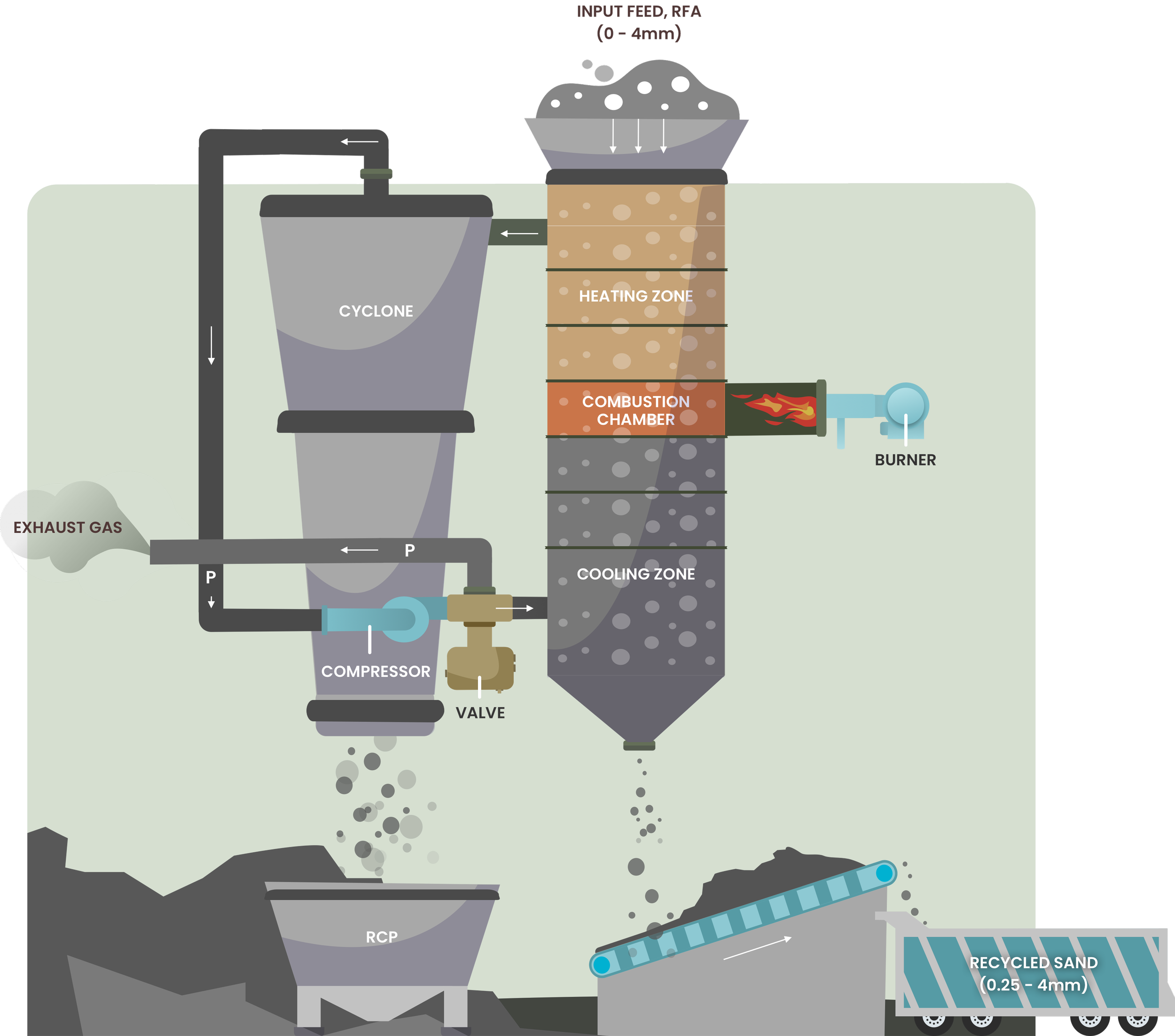
Heating Air and classification System (HAS)
The HAS technology is designed to further expose the fine fraction aggregates (0-4mm) into a hot gas (~500 °C) to remove the associated moisture, destroy undesirable CDW contaminants (mainly wood and plastics) to produce clean sand (≥ 0.25 – 4 mm) and recycled cement paste product (≤ 0.25 mm).
The entire process involves the interaction of particle-gas system in a fluidized-type reactor, where the air is used to carry the heat and, at the same time, classify EOL concrete aggregates based on their particle size. The impact of heating is to remove the moisture and also to activate and disintegrate the surface of the recycled cement paste.
While the airflow drags the ultrafine particles, the heavier and coarse particles are collected at the bottom of the HAS. The HAS technology is based on a gravitational-counterflow zone, where the classifier is designed around a rising airflow inside a vertical chamber. The aggregate particles fall from the top of the chamber, and the drag force acts in the opposite direction to gravity. Coarse particles will continue downwards while fines will be carried out by airflow, as shown in Figure 3.